Signed in as:
filler@godaddy.com
Signed in as:
filler@godaddy.com
Our core Java programming tutorial is designed for students and working professionals. Java is an object-oriented, class-based, concurrent, secured and general-purpose computer-programming language. It is a widely used robust technology.
Java is a programming language and a platform. Java is a high level, robust, object-oriented and secure programming language.
Java was developed by Sun Microsystems (which is now the subsidiary of Oracle) in the year 1995. James Gosling is known as the father of Java. Before Java, its name was Oak. Since Oak was already a registered company, so James Gosling and his team changed the name from Oak to Java.
Platform: Any hardware or software environment in which a program runs, is known as a platform. Since Java has a runtime environment (JRE) and API, it is called a platform.
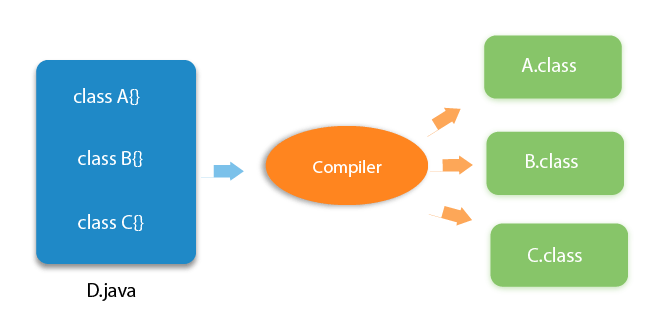
Let's have a quick look at Java programming example. A detailed description of Hello Java example is available in next page.
Simple.java
Test it Now
According to Sun, 3 billion devices run Java. There are many devices where Java is currently used. Some of them are as follows:
ADAD
There are mainly 4 types of applications that can be created using Java programming:
Standalone applications are also known as desktop applications or window-based applications. These are traditional software that we need to install on every machine. Examples of standalone application are Media player, antivirus, etc. AWT and Swing are used in Java for creating standalone applications.
An application that runs on the server side and creates a dynamic page is called a web application. Currently, Servlet, JSP, Struts, Spring, Hibernate, JSF, etc. technologies are used for creating web applications in Java.
An application that is distributed in nature, such as banking applications, etc. is called an enterprise application. It has advantages like high-level security, load balancing, and clustering. In Java, EJB is used for creating enterprise applications.
An application which is created for mobile devices is called a mobile application. Currently, Android and Java ME are used for creating mobile applications.
There are 4 platforms or editions of Java:
It is a Java programming platform. It includes Java programming APIs such as java.lang, java.io, java.net, java.util, java.sql, java.math etc. It includes core topics like OOPs, String, Regex, Exception, Inner classes, Multithreading, I/O Stream, Networking, AWT, Swing, Reflection, Collection, etc.
It is an enterprise platform that is mainly used to develop web and enterprise applications. It is built on top of the Java SE platform. It includes topics like Servlet, JSP, Web Services, EJB, JPA, etc.
It is a micro platform that is dedicated to mobile applications.
It is used to develop rich internet applications. It uses a lightweight user interface API.
ADAD
To learn Java, you must have the basic knowledge of C/C++ programming language.
Our Java programming tutorial is designed to help beginners and professionals.
We assure that you will not find any problem in this Java tutorial. However, if there is any mistake, please post the problem in the contact form.
Do You Know?
What will we learn in Basics of Java?
=============================================================================
The history of Java is very interesting. Java was originally designed for interactive television, but it was too advanced technology for the digital cable television industry at the time. The history of Java starts with the Green Team. Java team members (also known as Green Team), initiated this project to develop a language for digital devices such as set-top boxes, televisions, etc. However, it was best suited for internet programming. Later, Java technology was incorporated by Netscape.
The principles for creating Java programming were "Simple, Robust, Portable, Platform-independent, Secured, High Performance, Multithreaded, Architecture Neutral, Object-Oriented, Interpreted, and Dynamic". Java was developed by James Gosling, who is known as the father of Java, in 1995. James Gosling and his team members started the project in the early '90s.

Currently, Java is used in internet programming, mobile devices, games, e-business solutions, etc. Following are given significant points that describe the history of Java.
1) James Gosling, Mike Sheridan, and Patrick Naughton initiated the Java language project in June 1991. The small team of sun engineers called Green Team.
2) Initially it was designed for small, embedded systems in electronic appliances like set-top boxes.
3) Firstly, it was called "Greentalk" by James Gosling, and the file extension was .gt.
4) After that, it was called Oak and was developed as a part of the Green project.

5) Why Oak? Oak is a symbol of strength and chosen as a national tree of many countries like the U.S.A., France, Germany, Romania, etc.
6) In 1995, Oak was renamed as "Java" because it was already a trademark by Oak Technologies.
7) Why had they chose the name Java for Java language? The team gathered to choose a new name. The suggested words were "dynamic", "revolutionary", "Silk", "jolt", "DNA", etc. They wanted something that reflected the essence of the technology: revolutionary, dynamic, lively, cool, unique, and easy to spell, and fun to say.
According to James Gosling, "Java was one of the top choices along with Silk". Since Java was so unique, most of the team members preferred Java than other names.
8) Java is an island in Indonesia where the first coffee was produced (called Java coffee). It is a kind of espresso bean. Java name was chosen by James Gosling while having a cup of coffee nearby his office.
9) Notice that Java is just a name, not an acronym.
10) Initially developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems (which is now a subsidiary of Oracle Corporation) and released in 1995.
11) In 1995, Time magazine called Java one of the Ten Best Products of 1995.
12) JDK 1.0 was released on January 23, 1996. After the first release of Java, there have been many additional features added to the language. Now Java is being used in Windows applications, Web applications, enterprise applications, mobile applications, cards, etc. Each new version adds new features in Java.
Many java versions have been released till now. The current stable release of Java is Java SE 10.
ADAD
Since Java SE 8 release, the Oracle corporation follows a pattern in which every even version is release in March month and an odd version released in September month.
==============================================================================
The primary objective of Java programming language creation was to make it portable, simple and secure programming language. Apart from this, there are also some excellent features which play an important role in the popularity of this language. The features of Java are also known as Java buzzwords.
A list of the most important features of the Java language is given below.
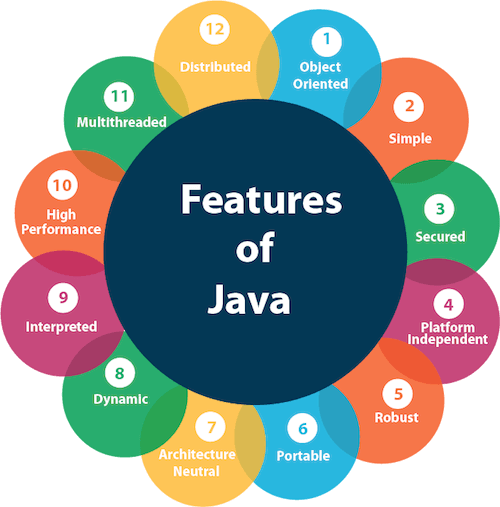
Java is very easy to learn, and its syntax is simple, clean and easy to understand. According to Sun Microsystem, Java language is a simple programming language because:
Java is an object-oriented programming language. Everything in Java is an object. Object-oriented means we organize our software as a combination of different types of objects that incorporate both data and behavior.
Object-oriented programming (OOPs) is a methodology that simplifies software development and maintenance by providing some rules.
Basic concepts of OOPs are:

Java is platform independent because it is different from other languages like C, C++, etc. which are compiled into platform specific machines while Java is a write once, run anywhere language. A platform is the hardware or software environment in which a program runs.
There are two types of platforms software-based and hardware-based. Java provides a software-based platform.
The Java platform differs from most other platforms in the sense that it is a software-based platform that runs on top of other hardware-based platforms. It has two components:
Java code can be executed on multiple platforms, for example, Windows, Linux, Sun Solaris, Mac/OS, etc. Java code is compiled by the compiler and converted into bytecode. This bytecode is a platform-independent code because it can be run on multiple platforms, i.e., Write Once and Run Anywhere (WORA).
Java is best known for its security. With Java, we can develop virus-free systems. Java is secured because:
ADAD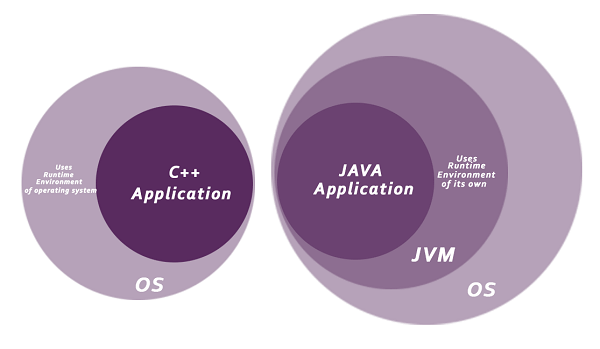
Java language provides these securities by default. Some security can also be provided by an application developer explicitly through SSL, JAAS, Cryptography, etc.
The English mining of Robust is strong. Java is robust because:
Java is architecture neutral because there are no implementation dependent features, for example, the size of primitive types is fixed.
In C programming, int data type occupies 2 bytes of memory for 32-bit architecture and 4 bytes of memory for 64-bit architecture. However, it occupies 4 bytes of memory for both 32 and 64-bit architectures in Java.
Java is portable because it facilitates you to carry the Java bytecode to any platform. It doesn't require any implementation.
Java is faster than other traditional interpreted programming languages because Java bytecode is "close" to native code. It is still a little bit slower than a compiled language (e.g., C++). Java is an interpreted language that is why it is slower than compiled languages, e.g., C, C++, etc.
ADAD
Java is distributed because it facilitates users to create distributed applications in Java. RMI and EJB are used for creating distributed applications. This feature of Java makes us able to access files by calling the methods from any machine on the internet.
A thread is like a separate program, executing concurrently. We can write Java programs that deal with many tasks at once by defining multiple threads. The main advantage of multi-threading is that it doesn't occupy memory for each thread. It shares a common memory area. Threads are important for multi-media, Web applications, etc.
Java is a dynamic language. It supports the dynamic loading of classes. It means classes are loaded on demand. It also supports functions from its native languages, i.e., C and C++.
Java supports dynamic compilation and automatic memory management (garbage collection).
==============================================================================
In this section, we will learn how to write the simple program of Java. We can write a simple hello Java program easily after installing the JDK.
To create a simple Java program, you need to create a class that contains the main method. Let's understand the requirement first.
For executing any Java program, the following software or application must be properly installed.
Let's create the hello java program:
Test it Now
Save the above file as Simple.java.
To compile:javac Simple.javaTo execute:java Simple
Output:
Hello Java
Compilation Flow:
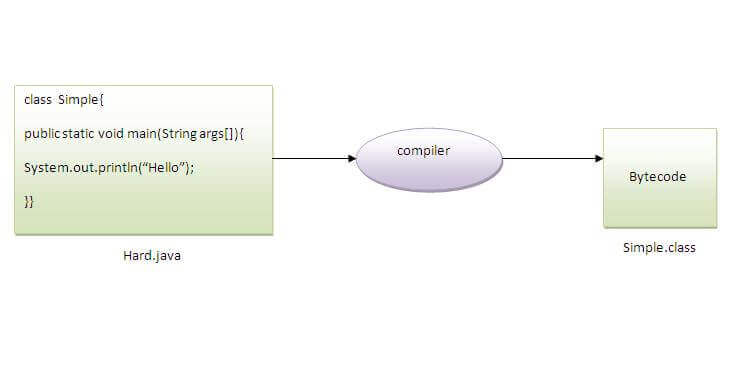
When we compile Java program using javac tool, the Java compiler converts the source code into byte code.
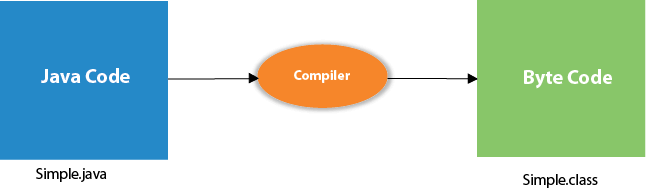
Let's see what is the meaning of class, public, static, void, main, String[], System.out.println().
ADAD
To write the simple program, you need to open notepad by start menu -> All Programs -> Accessories -> Notepad and write a simple program as we have shownbelow:
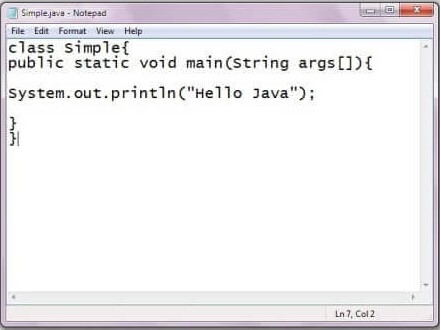
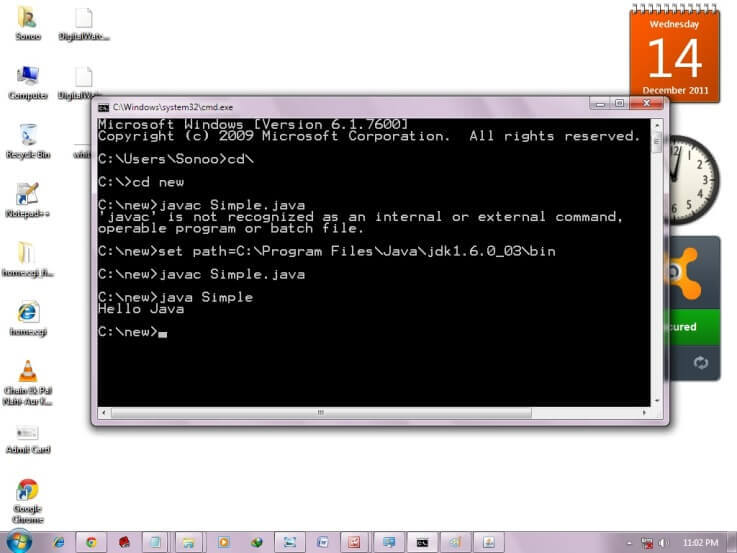
As displayed in the above diagram, write the simple program of Java in notepad and saved it as Simple.java. In order to compile and run the above program, you need to open the command prompt by start menu -> All Programs -> Accessories -> command prompt. When we have done with all the steps properly, it shows the following output:
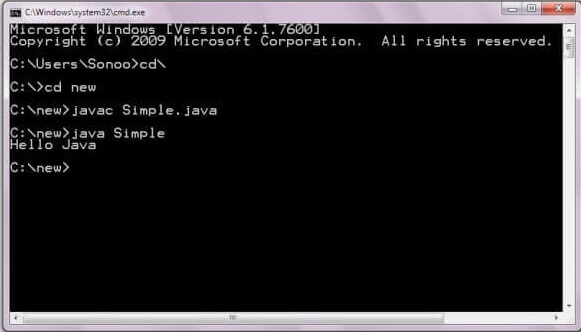
To compile and run the above program, go to your current directory first; my current directory is c:\new. Write here:
To compile:javac Simple.javaTo execute:java Simple
There are many ways to write a Java program. The modifications that can be done in a Java program are given below:
1) By changing the sequence of the modifiers, method prototype is not changed in Java.
Let's see the simple code of the main method.
2) The subscript notation in the Java array can be used after type, before the variable or after the variable.
ADAD
Let's see the different codes to write the main method.
3) You can provide var-args support to the main() method by passing 3 ellipses (dots)
Let's see the simple code of using var-args in the main() method. We will learn about var-args later in the Java New Features chapter.
4) Having a semicolon at the end of class is optional in Java.
Let's see the simple code.
ADAD
ADAD
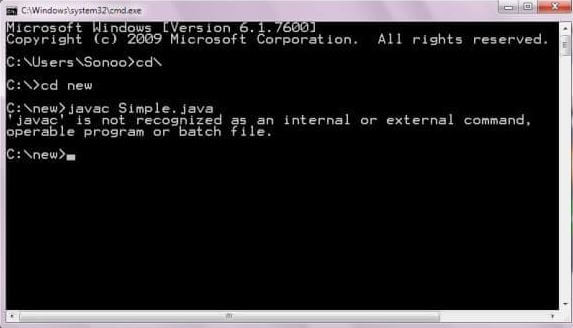
If there occurs a problem like displayed in the below figure, you need to set a path. Since DOS doesn't recognize javac and java as internal or external command. To overcome this problem, we need to set a path. The path is not required in a case where you save your program inside the JDK/bin directory. However, it is an excellent approach to set the path. Click here for How to set path in java.
==============================================================================
In the previous section, we have created Java Hello World program and learn how to compile and run a Java program. In this section, we are going to learn, what happens while we compile and run the Java program. Moreover, we will see some questions based on the first program.
At compile time, the Java file is compiled by Java Compiler (It does not interact with OS) and converts the Java code into bytecode.

At runtime, the following steps are performed:
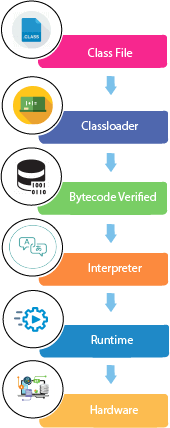
Classloader: It is the subsystem of JVM that is used to load class files.
Bytecode Verifier: Checks the code fragments for illegal code that can violate access rights to objects.
Interpreter: Read bytecode stream then execute the instructions.
Yes, if the class is not public. It is explained in the figure given below:
Observe that, we have compiled the code with file name but running the program with class name. Therefore, we can save a Java program other than class name.
Yes, like the figure given below illustrates:
==============================================================================
The path is required to be set for using tools such as javac, java, etc.
If you are saving the Java source file inside the JDK/bin directory, the path is not required to be set because all the tools will be available in the current directory.
However, if you have your Java file outside the JDK/bin folder, it is necessary to set the path of JDK.
There are two ways to set the path in Java:
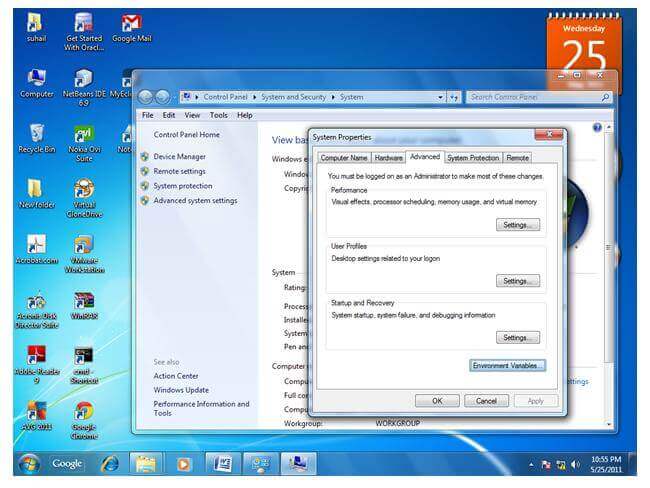
To set the temporary path of JDK, you need to follow the following steps:
set path=C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.6.0_23\bin
Let's see it in the figure given below:
For setting the permanent path of JDK, you need to follow these steps:
ADAD
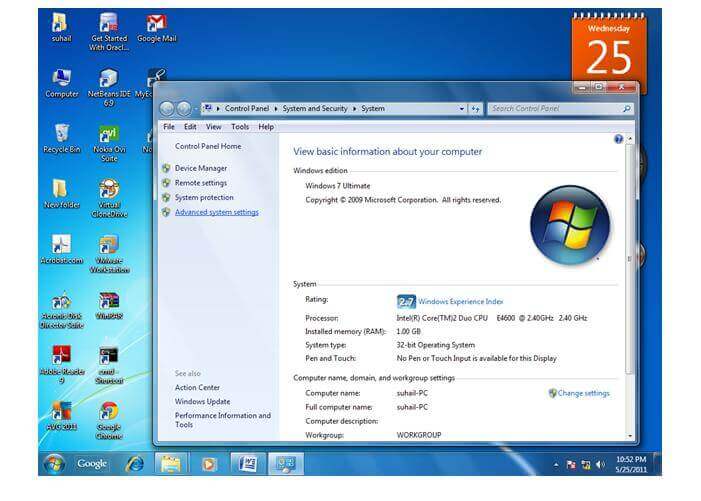
1) Go to MyComputer properties
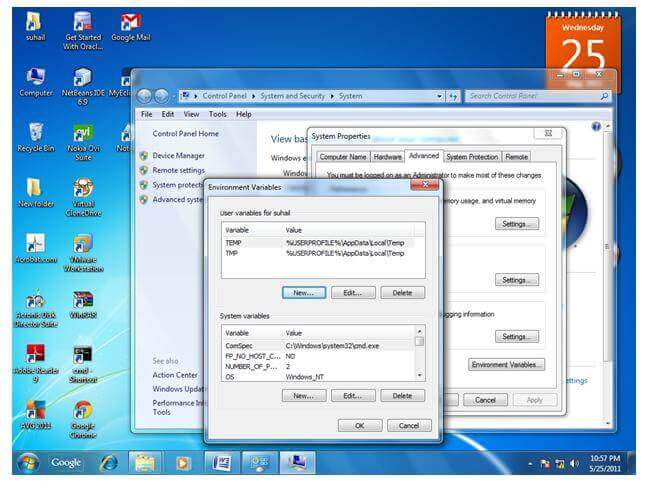
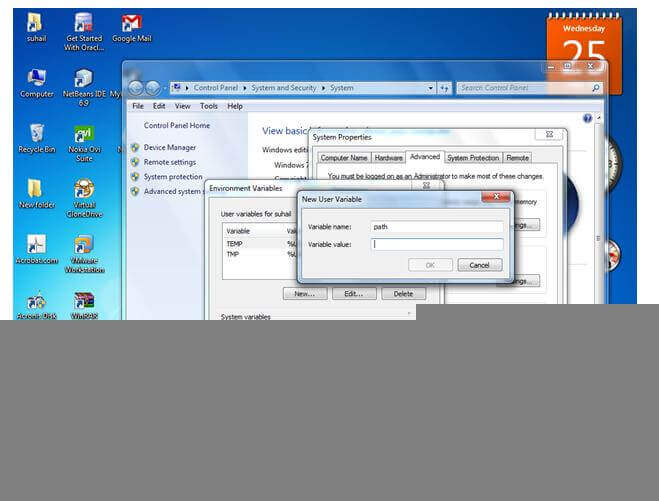
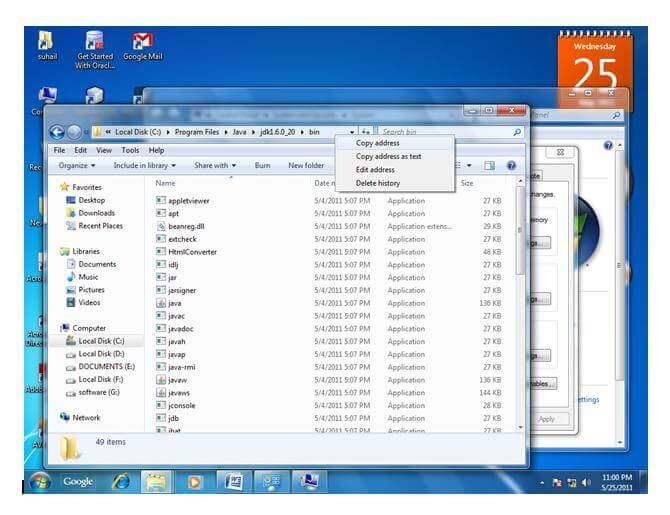
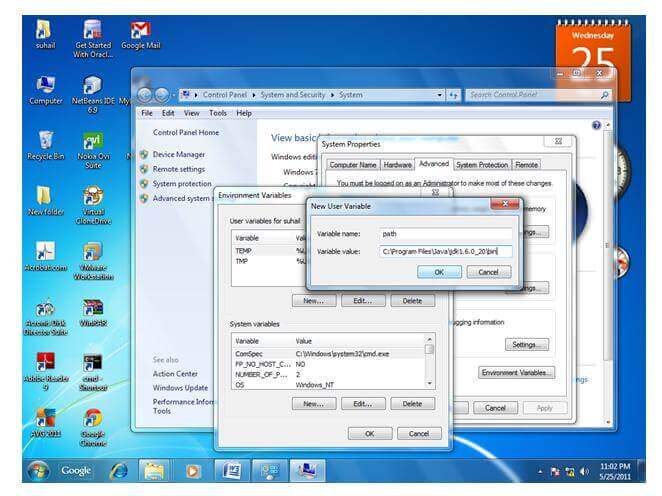
Now your permanent path is set. You can now execute any program of java from any drive.
Setting path in Linux OS is the same as setting the path in the Windows OS. But, here we use the export tool rather than set. Let's see how to set path in Linux OS:
export PATH=$PATH:/home/jdk1.6.01/bin/
Here, we have installed the JDK in the home directory under Root (/home).
You may also like:
How to set classpath in Java
==============================================================================
We must understand the differences between JDK, JRE, and JVM before proceeding further to Java. See the brief overview of JVM here.
If you want to get the detailed knowledge of Java Virtual Machine, move to the next page. Firstly, let's see the differences between the JDK, JRE, and JVM.
JVM (Java Virtual Machine) is an abstract machine. It is called a virtual machine because it doesn't physically exist. It is a specification that provides a runtime environment in which Java bytecode can be executed. It can also run those programs which are written in other languages and compiled to Java bytecode.
JVMs are available for many hardware and software platforms. JVM, JRE, and JDK are platform dependent because the configuration of each OS is different from each other. However, Java is platform independent. There are three notions of the JVM: specification, implementation, and instance.
The JVM performs the following main tasks:
More Details.
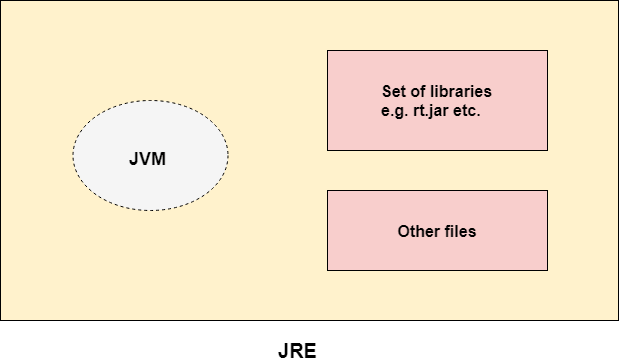
JRE is an acronym for Java Runtime Environment. It is also written as Java RTE. The Java Runtime Environment is a set of software tools which are used for developing Java applications. It is used to provide the runtime environment. It is the implementation of JVM. It physically exists. It contains a set of libraries + other files that JVM uses at runtime.
The implementation of JVM is also actively released by other companies besides Sun Micro Systems.
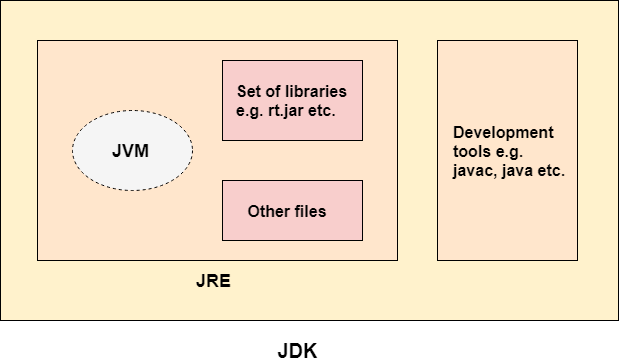
JDK is an acronym for Java Development Kit. The Java Development Kit (JDK) is a software development environment which is used to develop Java applications and applets. It physically exists. It contains JRE + development tools.
JDK is an implementation of any one of the below given Java Platforms released by Oracle Corporation:
ADAD
The JDK contains a private Java Virtual Machine (JVM) and a few other resources such as an interpreter/loader (java), a compiler (javac), an archiver (jar), a documentation generator (Javadoc), etc. to complete the development of a Java Application.
=============================================================================
JVM (Java Virtual Machine) is an abstract machine. It is a specification that provides runtime environment in which java bytecode can be executed.
JVMs are available for many hardware and software platforms (i.e. JVM is platform dependent).
It is:
The JVM performs following operation:
JVM provides definitions for the:
Let's understand the internal architecture of JVM. It contains classloader, memory area, execution engine etc.
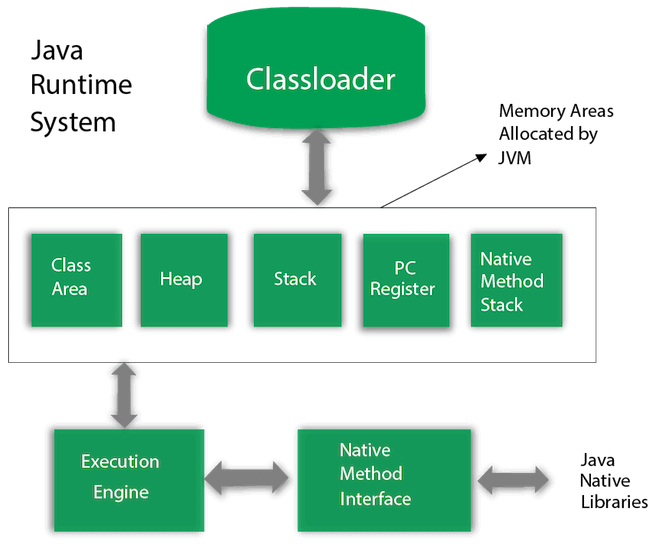
Classloader is a subsystem of JVM which is used to load class files. Whenever we run the java program, it is loaded first by the classloader. There are three built-in classloaders in Java.
Test it Now
Output:
sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@4e0e2f2a
null
These are the internal classloaders provided by Java. If you want to create your own classloader, you need to extend the ClassLoader class.
Class(Method) Area stores per-class structures such as the runtime constant pool, field and method data, the code for methods.
It is the runtime data area in which objects are allocated.
Java Stack stores frames. It holds local variables and partial results, and plays a part in method invocation and return.
Each thread has a private JVM stack, created at the same time as thread.
A new frame is created each time a method is invoked. A frame is destroyed when its method invocation completes.
PC (program counter) register contains the address of the Java virtual machine instruction currently being executed.
It contains all the native methods used in the application.
It contains:
Java Native Interface (JNI) is a framework which provides an interface to communicate with another application written in another language like C, C++, Assembly etc. Java uses JNI framework to send output to the Console or interact with OS libraries.
==============================================================================
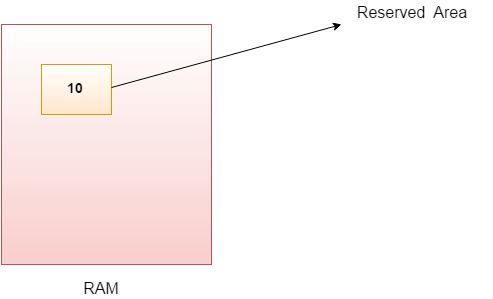
A variable is a container which holds the value while the Java program is executed. A variable is assigned with a data type.
Variable is a name of memory location. There are three types of variables in java: local, instance and static.
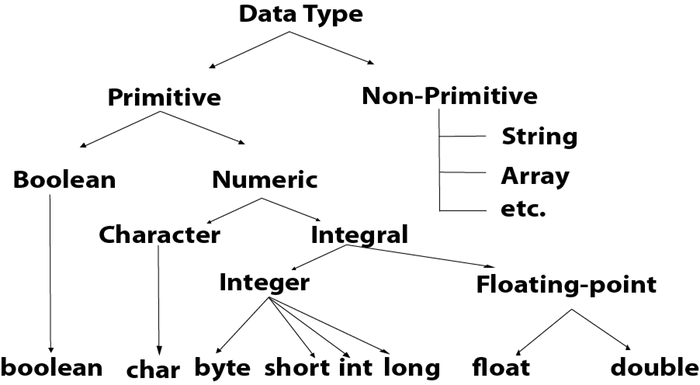
There are two types of data types in Java: primitive and non-primitive.
A variable is the name of a reserved area allocated in memory. In other words, it is a name of the memory location. It is a combination of "vary + able" which means its value can be changed.
There are three types of variables in Java:
A variable declared inside the body of the method is called local variable. You can use this variable only within that method and the other methods in the class aren't even aware that the variable exists.
A local variable cannot be defined with "static" keyword.
A variable declared inside the class but outside the body of the method, is called an instance variable. It is not declared as static.
It is called an instance variable because its value is instance-specific and is not shared among instances.
A variable that is declared as static is called a static variable. It cannot be local. You can create a single copy of the static variable and share it among all the instances of the class. Memory allocation for static variables happens only once when the class is loaded in the memory.
Output:
20
Output:
10
10.0
Output:
10.5
10
Output:
130
-126
Output:
20
=============================================================================
Data types specify the different sizes and values that can be stored in the variable. There are two types of data types in Java:
In Java language, primitive data types are the building blocks of data manipulation. These are the most basic data types available in Java language.
Java is a statically-typed programming language. It means, all variables must be declared before its use. That is why we need to declare variable's type and name.
There are 8 types of primitive data types:
 Data TypeDefault ValueDefault sizebooleanfalse1 bitchar'\u0000'2 bytebyte01 byteshort02 byteint04 bytelong0L8 bytefloat0.0f4 bytedouble0.0d8 byte
Data TypeDefault ValueDefault sizebooleanfalse1 bitchar'\u0000'2 bytebyte01 byteshort02 byteint04 bytelong0L8 bytefloat0.0f4 bytedouble0.0d8 byte
The Boolean data type is used to store only two possible values: true and false. This data type is used for simple flags that track true/false conditions.
The Boolean data type specifies one bit of information, but its "size" can't be defined precisely.
Example:
The byte data type is an example of primitive data type. It isan 8-bit signed two's complement integer. Its value-range lies between -128 to 127 (inclusive). Its minimum value is -128 and maximum value is 127. Its default value is 0.
The byte data type is used to save memory in large arrays where the memory savings is most required. It saves space because a byte is 4 times smaller than an integer. It can also be used in place of "int" data type.
Example:
ADAD
The short data type is a 16-bit signed two's complement integer. Its value-range lies between -32,768 to 32,767 (inclusive). Its minimum value is -32,768 and maximum value is 32,767. Its default value is 0.
The short data type can also be used to save memory just like byte data type. A short data type is 2 times smaller than an integer.
Example:
The int data type is a 32-bit signed two's complement integer. Its value-range lies between - 2,147,483,648 (-2^31) to 2,147,483,647 (2^31 -1) (inclusive). Its minimum value is - 2,147,483,648and maximum value is 2,147,483,647. Its default value is 0.
The int data type is generally used as a default data type for integral values unless if there is no problem about memory.
Example:
The long data type is a 64-bit two's complement integer. Its value-range lies between -9,223,372,036,854,775,808(-2^63) to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807(2^63 -1)(inclusive). Its minimum value is - 9,223,372,036,854,775,808and maximum value is 9,223,372,036,854,775,807. Its default value is 0. The long data type is used when you need a range of values more than those provided by int.
ADAD
Example:
The float data type is a single-precision 32-bit IEEE 754 floating point.Its value range is unlimited. It is recommended to use a float (instead of double) if you need to save memory in large arrays of floating point numbers. The float data type should never be used for precise values, such as currency. Its default value is 0.0F.
Example:
The double data type is a double-precision 64-bit IEEE 754 floating point. Its value range is unlimited. The double data type is generally used for decimal values just like float. The double data type also should never be used for precise values, such as currency. Its default value is 0.0d.
Example:
ADAD
The char data type is a single 16-bit Unicode character. Its value-range lies between '\u0000' (or 0) to '\uffff' (or 65,535 inclusive).The char data type is used to store characters.
Example:
It is because java uses Unicode system not ASCII code system. The \u0000 is the lowest range of Unicode system. To get detail explanation about Unicode visit next page.
=============================================================================
Unicode is a universal international standard character encoding that is capable of representing most of the world's written languages.
Before Unicode, there were many language standards:
This caused two problems:
To solve these problems, a new language standard was developed i.e. Unicode System.In unicode, character holds 2 byte, so java also uses 2 byte for characters.lowest value:\u0000highest value:\uFFFF.
=============================================================================
Operator in Java is a symbol that is used to perform operations. For example: +, -, *, / etc.
There are many types of operators in Java which are given below:
Operator TypeCategoryPrecedenceUnarypostfixexpr++ expr--prefix++expr --expr +expr -expr ~ !Arithmeticmultiplicative* / %additive+ -Shiftshift<< >> >>>Relationalcomparison< > <= >= instanceofequality== !=Bitwisebitwise AND&bitwise exclusive OR^bitwise inclusive OR|Logicallogical AND&&logical OR||Ternaryternary? :Assignmentassignment= += -= *= /= %= &= ^= |= <<= >>= >>>=
The Java unary operators require only one operand. Unary operators are used to perform various operations i.e.:
ADAD
Output:
10
12
12
10
Output:
22
21
Output:
-11
9
false
true
Java arithmetic operators are used to perform addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. They act as basic mathematical operations.
Output:
15
5
50
2
0
Output:
21
The Java left shift operator << is used to shift all of the bits in a value to the left side of a specified number of times.
Output:
40
80
80
240
The Java right shift operator >> is used to move the value of the left operand to right by the number of bits specified by the right operand.
Output:
2
5
2
Output:
5
5
-5
1073741819
The logical && operator doesn't check the second condition if the first condition is false. It checks the second condition only if the first one is true.
The bitwise & operator always checks both conditions whether first condition is true or false.
ADAD
Output:
false
false
Output:
false
10
false
11
The logical || operator doesn't check the second condition if the first condition is true. It checks the second condition only if the first one is false.
The bitwise | operator always checks both conditions whether first condition is true or false.
Output:
ADAD
true
true
true
10
true
11
Java Ternary operator is used as one line replacement for if-then-else statement and used a lot in Java programming. It is the only conditional operator which takes three operands.
Output:
2
Another Example:
Output:
5
Java assignment operator is one of the most common operators. It is used to assign the value on its right to the operand on its left.
Output:
14
16
Output:
13
9
18
9
Output:
Compile time error
After type cast:
Output:
20
We use cookies to analyze website traffic and optimize your website experience. By accepting our use of cookies, your data will be aggregated with all other user data.