Signed in as:
filler@godaddy.com
Signed in as:
filler@godaddy.com
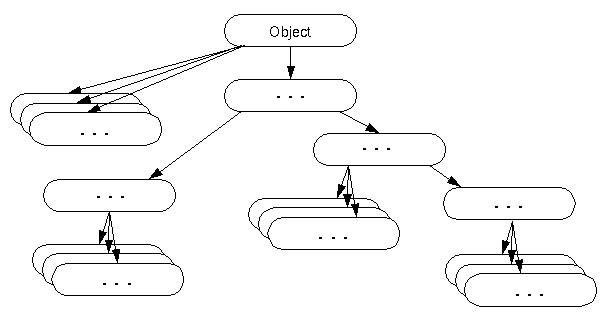
The Object class is the parent class of all the classes in java by default. In other words, it is the topmost class of java.
The Object class is beneficial if you want to refer any object whose type you don't know. Notice that parent class reference variable can refer the child class object, know as upcasting.
Let's take an example, there is getObject() method that returns an object but it can be of any type like Employee,Student etc, we can use Object class reference to refer that object. For example:
The Object class provides some common behaviors to all the objects such as object can be compared, object can be cloned, object can be notified etc.
The Object class provides many methods. They are as follows :
1) public final Class getClass( ) : Returns the Class class object of this object. The Class class can further be used to get the metadata of this class.
2) public int hashCode() : returns the hashcode number for this object.public boolean equals(Object obj)compares the given object to this object.
3) protected Object clone() : throws CloneNotSupportedExceptioncreates and returns the exact copy (clone) of this object.
4) public String toString() : returns the string representation of this object.
5) public final void notify() : wakes up single thread, waiting on this object's monitor.
6) public final void notifyAll() : wakes up all the threads, waiting on this object's monitor.
7) public final void wait(long timeout)throws InterruptedExceptioncauses : the current thread to wait for the specified milliseconds, until another thread notifies (invokes notify() or notifyAll() method).
8) public final void wait(long timeout,int nanos)throws InterruptedExceptioncauses : the current thread to wait for the specified milliseconds and nanoseconds, until another thread notifies (invokes notify() or notifyAll() method).
9) public final void wait()throws : InterruptedExceptioncauses the current thread to wait, until another thread notifies (invokes notify() or notifyAll() method).
10) protected void finalize()throws : Throwableis invoked by the garbage collector before object is being garbage collected.
============================================================================
The object cloning is a way to create exact copy of an object. The clone() method of Object class is used to clone an object.
The java.lang.Cloneable interface must be implemented by the class whose object clone we want to create. If we don't implement Cloneable interface, clone() method generates CloneNotSupportedException.
The clone() method is defined in the Object class. Syntax of the clone() method is as follows:
The clone() method saves the extra processing task for creating the exact copy of an object. If we perform it by using the new keyword, it will take a lot of processing time to be performed that is why we use object cloning.
Although Object.clone() has some design issues but it is still a popular and easy way of copying objects. Following is a list of advantages of using clone() method:
Following is a list of some disadvantages of clone() method:
Let's see the simple example of object cloning
Test it Now
Output:101 amit
101 amit
download the example of object cloning
As you can see in the above example, both reference variables have the same value. Thus, the clone() copies the values of an object to another. So we don't need to write explicit code to copy the value of an object to another.
If we create another object by new keyword and assign the values of another object to this one, it will require a lot of processing on this object. So to save the extra processing task we use clone() method.
===========================================================================
Java Math class provides several methods to work on math calculations like min(), max(), avg(), sin(), cos(), tan(), round(), ceil(), floor(), abs() etc.
Unlike some of the StrictMath class numeric methods, all implementations of the equivalent function of Math class can't define to return the bit-for-bit same results. This relaxation permits implementation with better-performance where strict reproducibility is not required.
If the size is int or long and the results overflow the range of value, the methods addExact(), subtractExact(), multiplyExact(), and toIntExact() throw an ArithmeticException.
For other arithmetic operations like increment, decrement, divide, absolute value, and negation overflow occur only with a specific minimum or maximum value. It should be checked against the maximum and minimum value as appropriate.
Test it Now
Output:
Maximum number of x and y is: 28.0
Square root of y is: 2.0
Power of x and y is: 614656.0
Logarithm of x is: 3.332204510175204
Logarithm of y is: 1.3862943611198906
log10 of x is: 1.4471580313422192
log10 of y is: 0.6020599913279624
log1p of x is: 3.367295829986474
exp of a is: 1.446257064291475E12
expm1 of a is: 1.446257064290475E12
Test it Now
Output:
Sine value of a is: -0.9880316240928618
Cosine value of a is: 0.15425144988758405
Tangent value of a is: -6.405331196646276
Sine value of a is: NaN
Cosine value of a is: NaN
Tangent value of a is: 1.5374753309166493
Sine value of a is: 5.343237290762231E12
Cosine value of a is: 5.343237290762231E12
Tangent value of a is: 1.0
The java.lang.Math class contains various methods for performing basic numeric operations such as the logarithm, cube root, and trigonometric functions etc. The various java math methods are as follows:
Math.abs() : It will return the Absolute value of the given value.
Math.max() : It returns the Largest of two values.
Math.min() : It is used to return the Smallest of two values.
:Math.round() It is used to round of the decimal numbers to the nearest value. It is used to round of the decimal numbers to the nearest value.
Math.sqrt() : It is used to return the square root of a number.
Math.cbrt() : It is used to return the cube root of a number.
Math.pow() : It returns the value of first argument raised to the power to second argument.
Math.signum() : It is used to find the sign of a given value.
Math.ceil() : It is used to find the smallest integer value that is greater than or equal to the argument or mathematical integer.
Math.copySign() : It is used to find the Absolute value of first argument along with sign specified in second argument.
Math.nextAfter() : It is used to return the floating-point number adjacent to the first argument in the direction of the second argument.
Math.nextUp() : It returns the floating-point value adjacent to d in the direction of positive infinity.
Math.nextDown( ) : It returns the floating-point value adjacent to d in the direction of negative infinity.
Math.floor() : It is used to find the largest integer value which is less than or equal to the argument and is equal to the mathematical integer of a double value.
Math.floorDiv() : It is used to find the largest integer value that is less than or equal to the algebraic quotient.
Math.random() : It returns a double value with a positive sign, greater than or equal to 0.0 and less than 1.0.
Math.rint() : It returns the double value that is closest to the given argument and equal to mathematical integer.
Math.hypot() : It returns sqrt(x2 +y2) without intermediate overflow or underflow.Math.ulp()It returns the size of an ulp of the argument.
Math.getExponent() : It is used to return the unbiased exponent used in the representation of a value.
Math.IEEEremainder() : It is used to calculate the remainder operation on two arguments as prescribed by the IEEE 754 standard and returns value.
Math.addExact() : It is used to return the sum of its arguments, throwing an exception if the result overflows an int or long.
Math.subtractExact() : It returns the difference of the arguments, throwing an exception if the result overflows an int.
Math.multiplyExact() : It is used to return the product of the arguments, throwing an exception if the result overflows an int or long.
Math.incrementExact() : It returns the argument incremented by one, throwing an exception if the result overflows an int.
Math.decrementExact() : It is used to return the argument decremented by one, throwing an exception if the result overflows an int or long.
Math.negateExact() : It is used to return the negation of the argument, throwing an exception if the result overflows an int or long.
Math.toIntExact() : It returns the value of the long argument, throwing an exception if the value overflows an int.
Math.log() : It returns the natural logarithm of a double value.
Math.log10() : It is used to return the base 10 logarithm of a double value.
Math.log1p() : It returns the natural logarithm of the sum of the argument and 1.
Math.exp() : It returns E raised to the power of a double value, where E is Euler's number and it is approximately equal to 2.71828.
Math.expm1() : It is used to calculate the power of E and subtract one from it.
Math.sin() : It is used to return the trigonometric Sine value of a Given double value.
Math.cos() : It is used to return the trigonometric Cosine value of a Given double value.
Math.tan() : It is used to return the trigonometric Tangent value of a Given double value.
Math.asin() : it is used to return the trigonometric Arc Sine value of a Given double value
Math.acos() : It is used to return the trigonometric Arc Cosine value of a Given double value.
Math.atan() : It is used to return the trigonometric Arc Tangent value of a Given double value
Math.sinh() : It is used to return the trigonometric Hyperbolic Cosine value of a Given double value.
Math.cosh() : It is used to return the trigonometric Hyperbolic Sine value of a Given double value.
Math.tanh() : It is used to return the trigonometric Hyperbolic Tangent value of a Given double value.
Math.toDegrees : It is used to convert the specified Radians angle to equivalent angle measured in Degrees.
Math.toRadians : It is used to convert the specified Degrees angle to equivalent angle measured in Radians.
We use cookies to analyze website traffic and optimize your website experience. By accepting our use of cookies, your data will be aggregated with all other user data.